ACTINOMORPHIC structures
Research on Innovative Parametric Construction Methodologies
'From 2d materials to 3d structures'
In the new Era of Digital Fabrication, this research aims to explore a parametric construction methodology that could transform 2d flexible flat materials into 3d rigid structures while visually underlining the aesthetic qualities of parametric design.
In the new Era of Digital Fabrication, this research aims to explore a parametric construction methodology that could transform 2d flexible flat materials into 3d rigid structures while visually underlining the aesthetic qualities of parametric design.
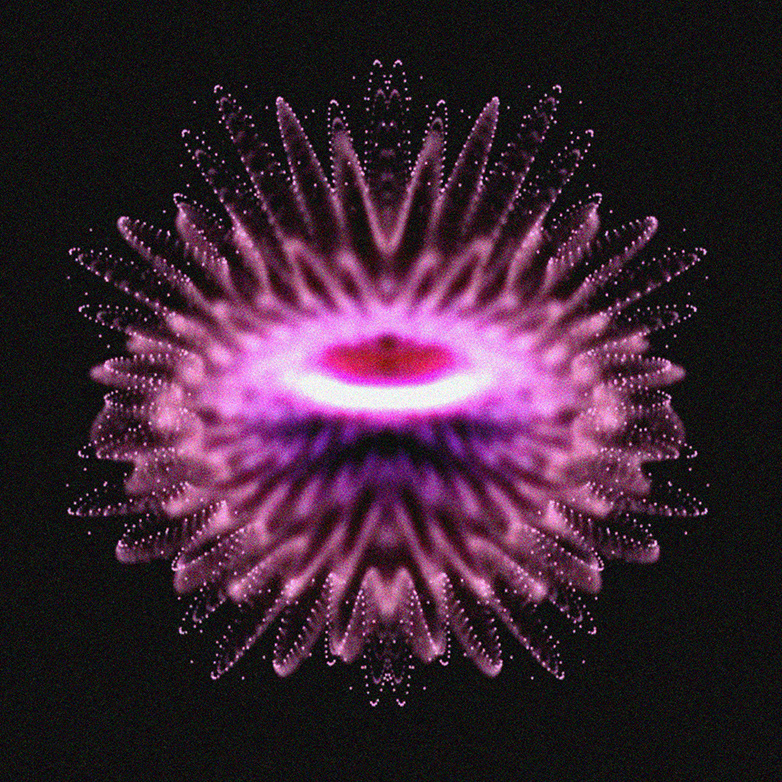
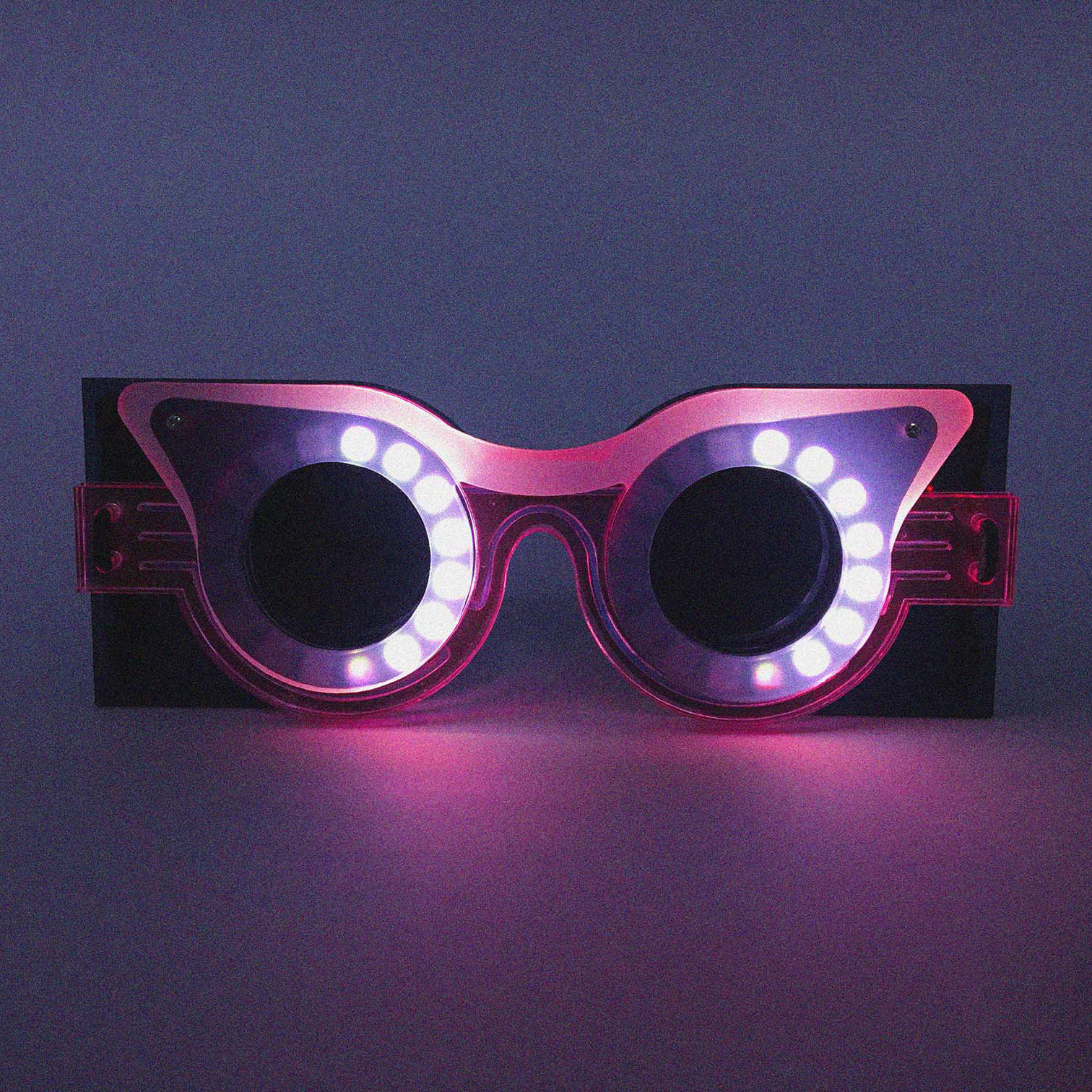
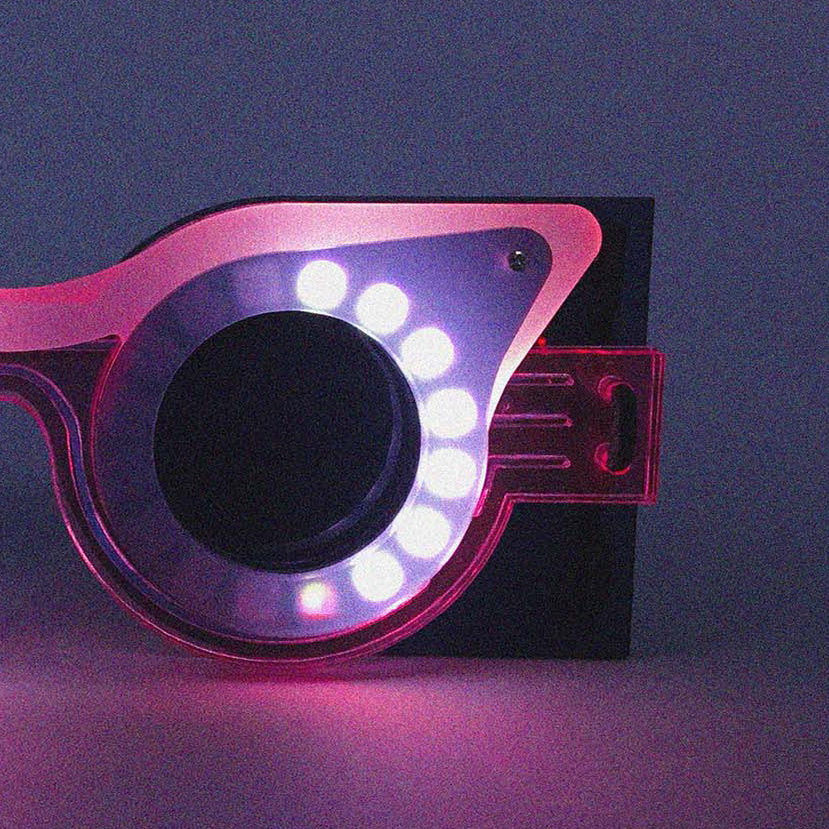
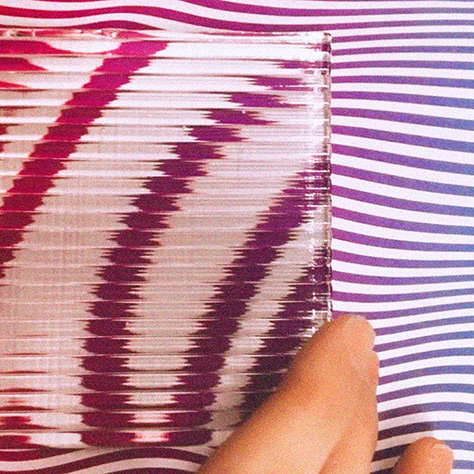
1. Flexible strip-shaped modules are an easy material to experiment with through digital fabrication processes.
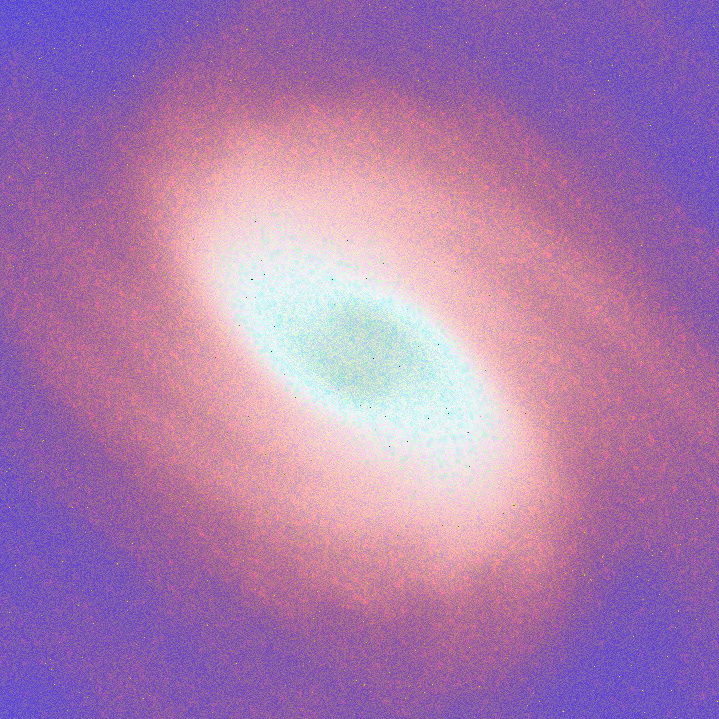
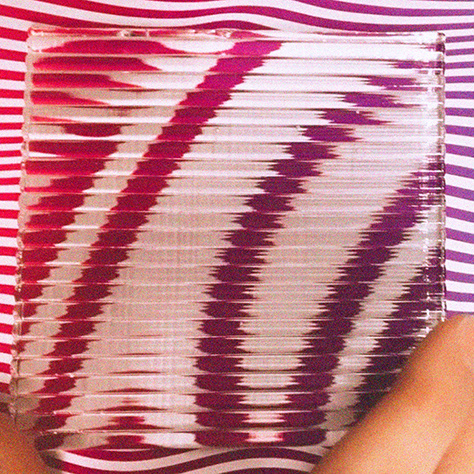
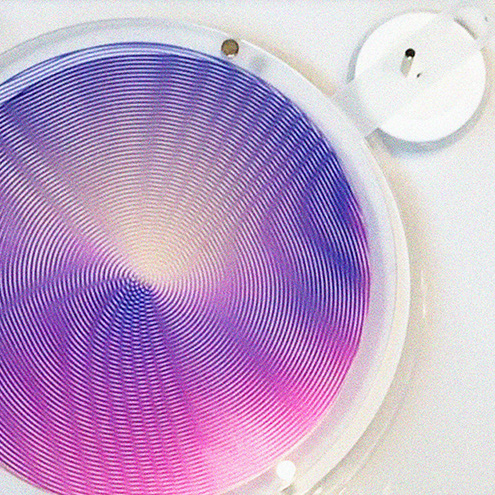
2. They are bended and jointed by applying the ‘eccentric loading error’ concept, obtaining a sinusoidal tensed shape, our “petals”.
3. In order to form a self-supporting structure, the petals are then closed along a central axis by following an actinomorphic symmetry, which ensure balance among tensions and resistances internal to the system.
2. They are bended and jointed by applying the ‘eccentric loading error’ concept, obtaining a sinusoidal tensed shape, our “petals”.
3. In order to form a self-supporting structure, the petals are then closed along a central axis by following an actinomorphic symmetry, which ensure balance among tensions and resistances internal to the system.
The parametric characteristic of this methodology allows to control several variables such as final shape, amount of petals, density of the sinusoidal joints, thickness of the material used, and, in general, the complexity of the output.
The fabrication process consists in laser-cut stripes from polypropylene sheets, jointed together with few different method such as interlocking joints, hand-sewn threads and cable ties.
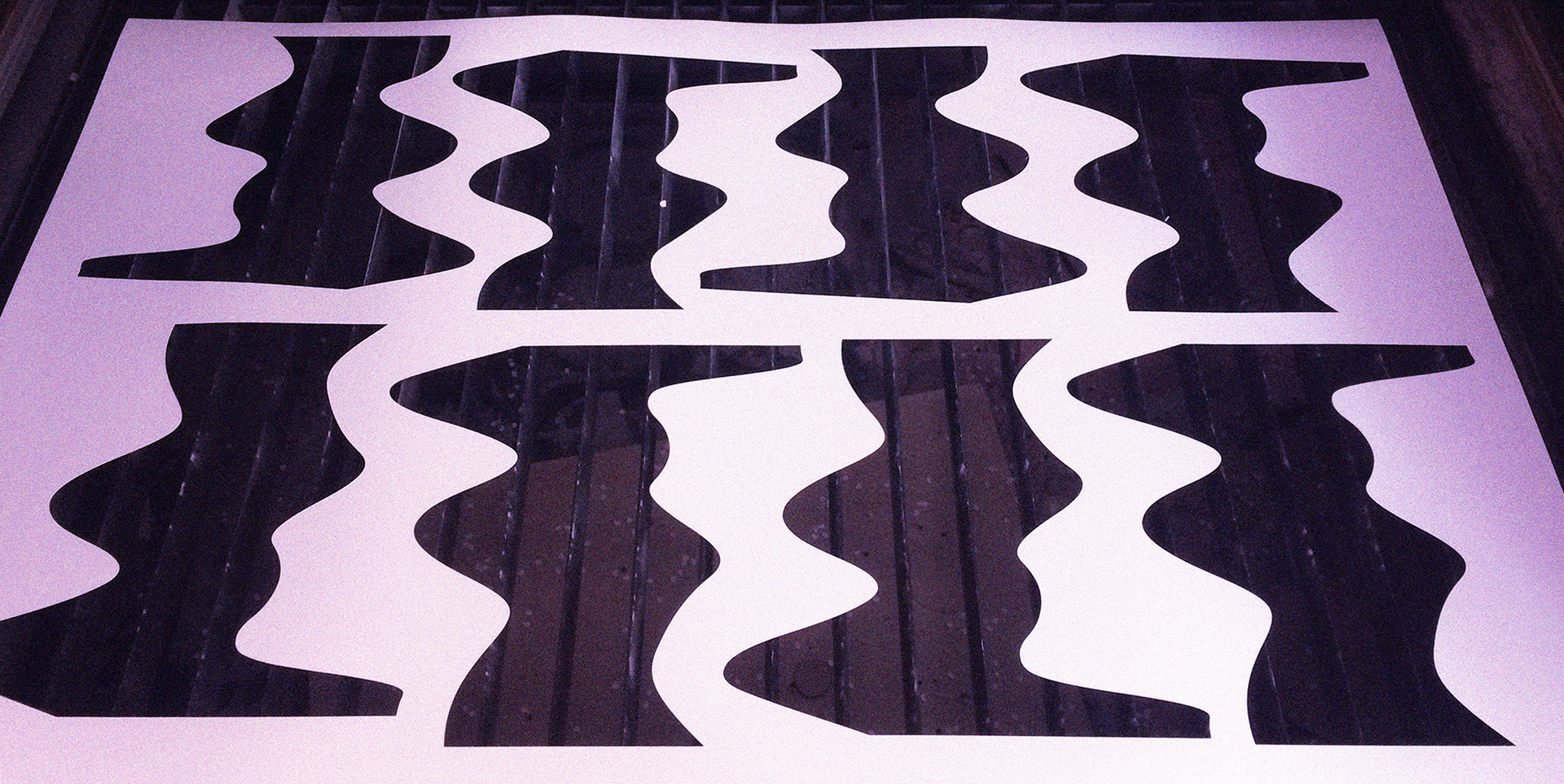

Laser-cut Process
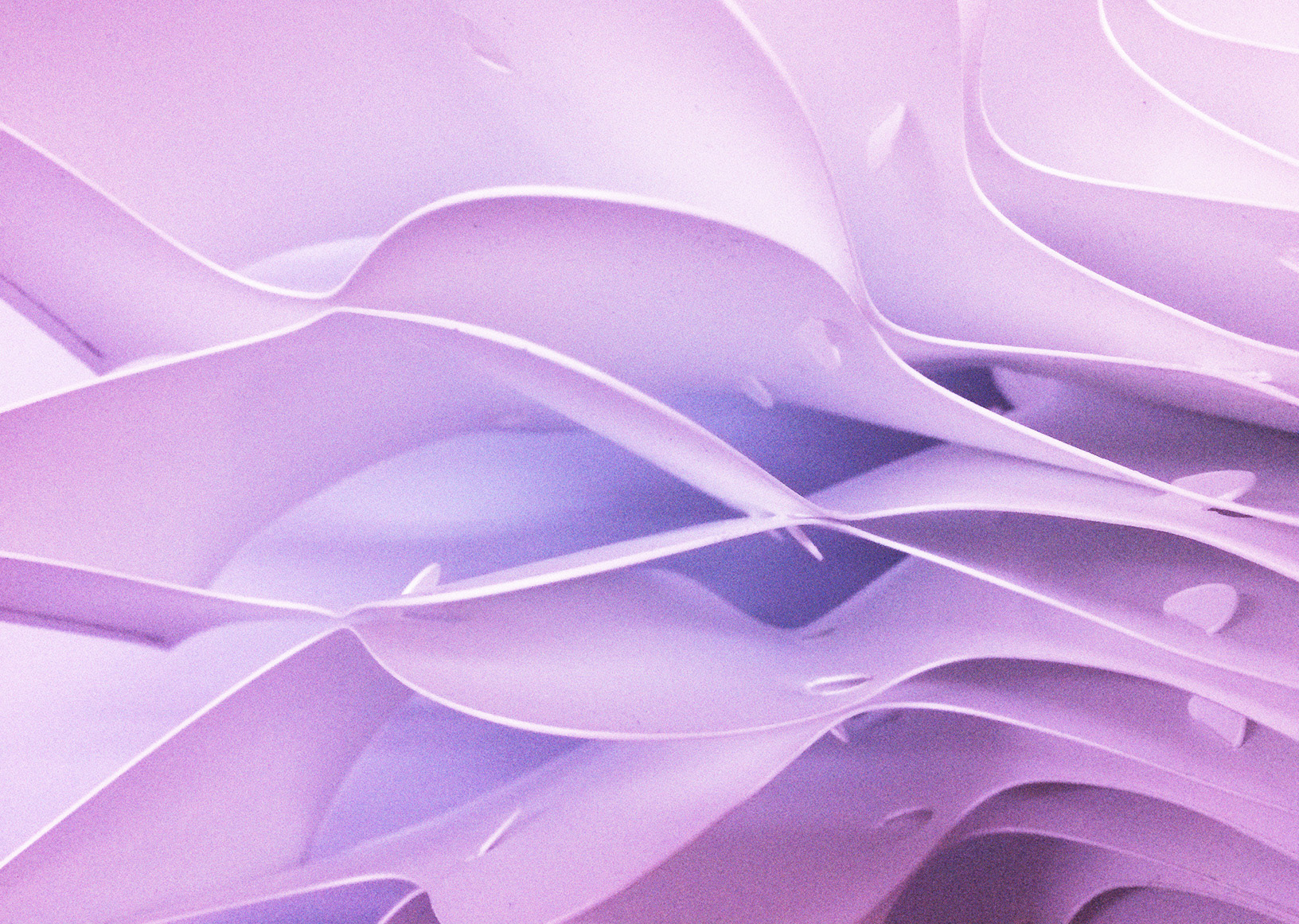

Interlocking Joints - Detail
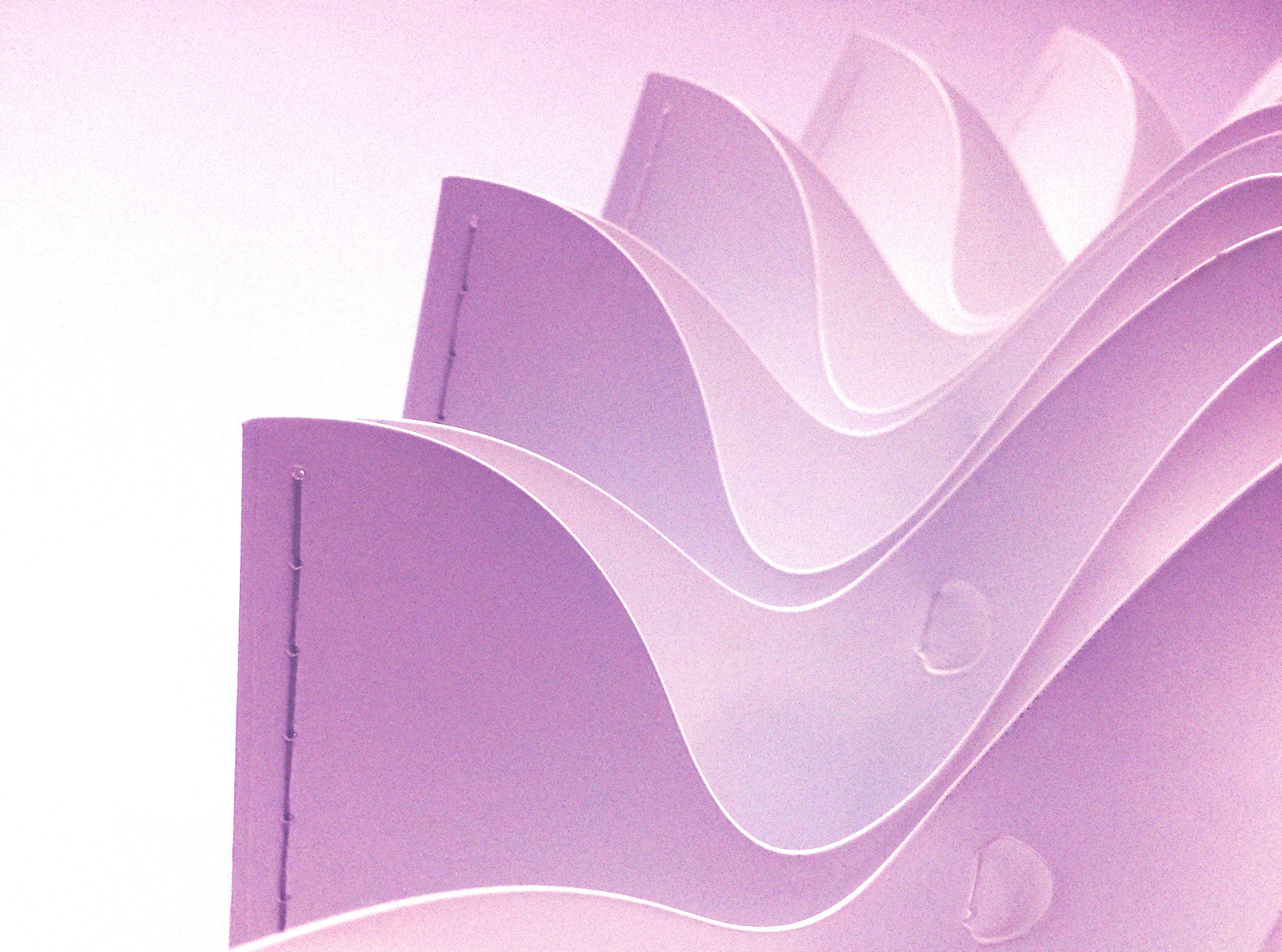

Hand Sewn Joints - Detail
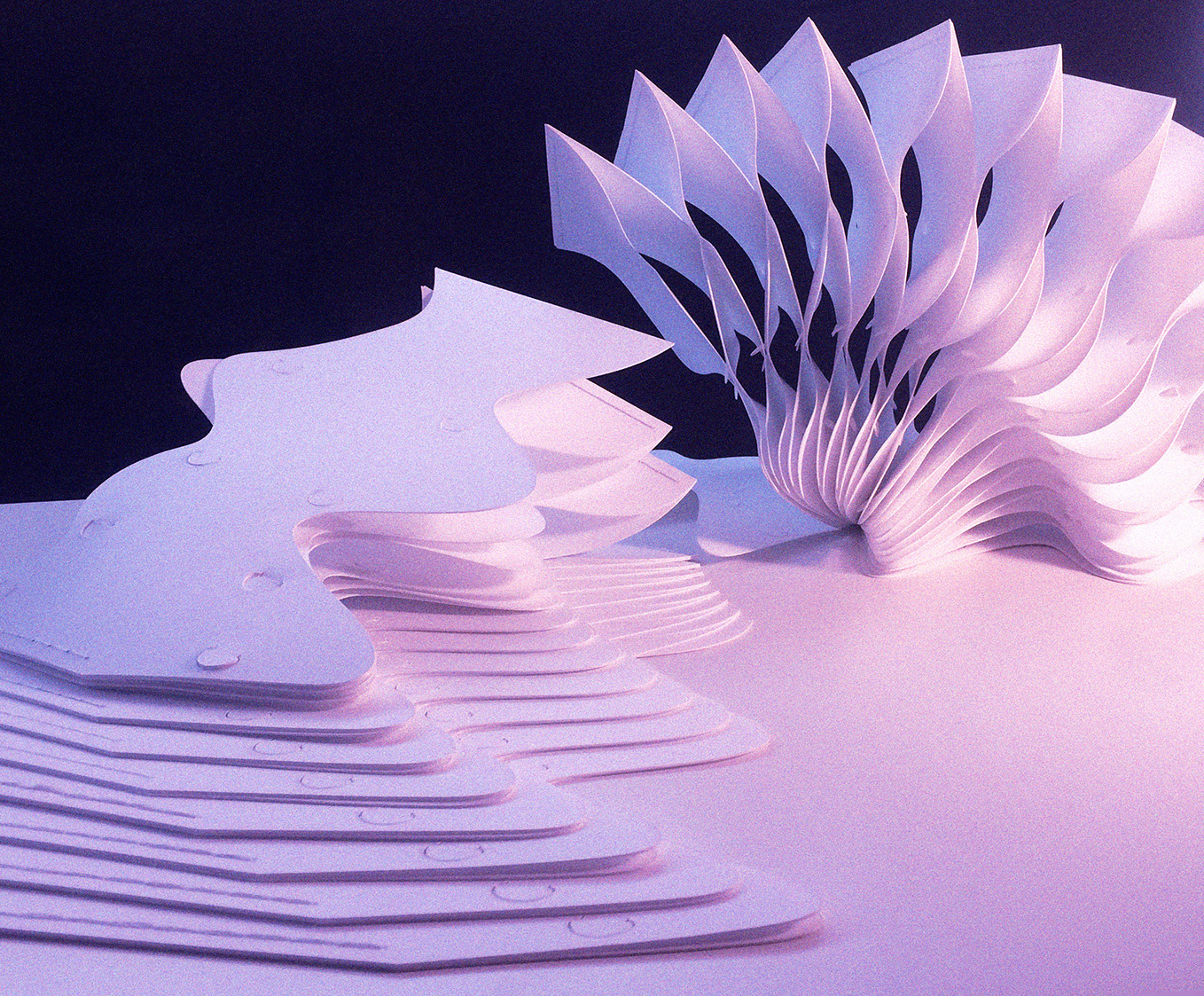
Assemby Process
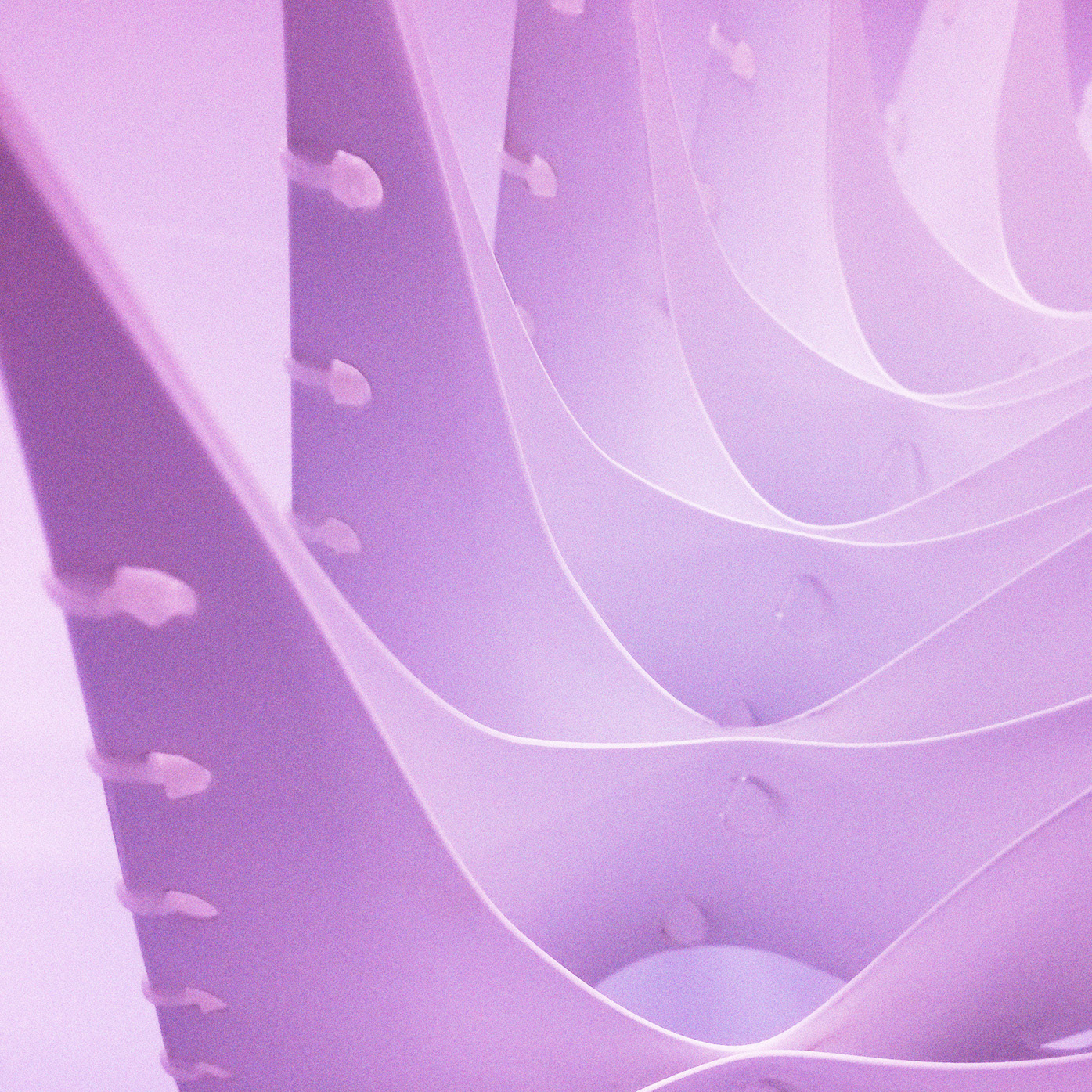

Cable Ties Joints - Detail